Samuel L. Jackson's Seville: A Badass History Tour

Tour Guide
Samuel L. Jackson
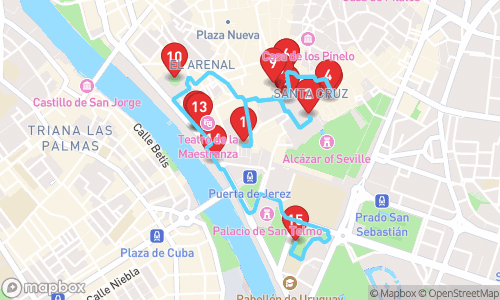
Welcome to Sevilla! On this GPS guided audio tour, we will visit 17 stops on a route of 3.16km. This tour focusses mainly on history.
Locatello is an app where you can generate personal audio guided tours. Set your preferred distance, guide, language and theme, and a guided tour is created on the spot.
Walking Time
Distance
stops
Language
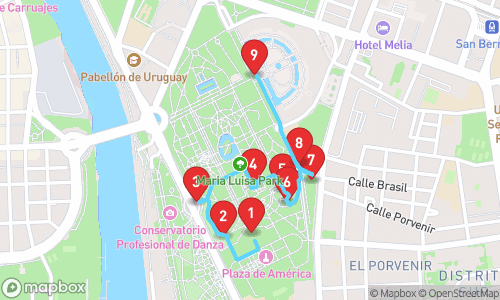
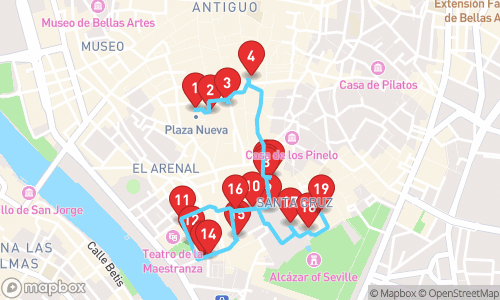
Tour Stops

Giraldillo
A sculpture, specifically the alegory of Fe, triumph of the church, crowning the Giralda of Seville, created in 1568 by Bartolomé Morel.

Tomb of Christopher Columbus (Seville)
A wooden tomb containing the remains of Christopher Columbus, a Spanish explorer and navigator who led the first European expeditions to the Americas. The tomb has been transferred several times during its history, including from Valladolid to Seville and from Santo Domingo to Havana.

Courtyard of the Orange Trees, Cathedral of Seville
A rectangular courtyard garden within the Seville Cathedral, built in 1172-1186, originally served as a traditional Muslim space for ceremonies, festivals, and burials with seven central arches and a Visigothic fountain.

Giralda
A striking bell tower, an iconic mixture of Moorish and Renaissance architecture in Seville, Spain, built as the minaret for the Great Mosque of Seville before being converted into a cathedral bell tower in the 16th century.

Antiguo Hospital de Venerables Sacerdotes
A former hospital turned museum, the Antiguo Hospital de Venerables Sacerdotes houses the Velázquez Center, dedicated to the life and works of Diego Velázquez. The center features exhibitions and artwork from the Golden Age of Spanish painting.

Reales Alcázares
A hydraulic structure, Reales Alcázares is a complex of palaces and gardens built by the Moorish and Gothic monarchs of Spain.

Plaza del Triunfo
A baroque square featuring the Triunfo de Nuestra Señora del Patrocinio temple, built in 1757 to commemorate the 1755 Lisbon earthquake, and a monument to the Inmaculada Concepción, dedicated to four influential Sevillian figures.
Audio Preview
30 sec
Catedral de Sevilla
Catholic cathedral in Seville, Andalusia, Spain, formerly a mosque, and a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1987.

Torre de Abdelazis
A hexagonal Almohade tower in Sevilla, Spain, formerly one of the city's wall vertices connecting to the nearby Real Alcázar palaces. It is also known as Torre del Homenaje, said to be the location where the Castilian flag was first raised after the city's conquest in 1248.

City walls of Seville
City walls of Seville: Expansion in the Islamic period: 9th-12th centuries. The walls were rebuilt and expanded during this period, doubling the city's walled enclosure, with multiple gates and courtyards designed to hinder sieges.

Torre de la Plata
A 13th-century octagonal military tower in Andalusia, constructed by the Almohad Caliphate, was linked by the city wall to another Moorish fortification, the Torre del Oro.

Seville Maritime Museum
A naval museum showcasing fossilized marine remains, navigation mechanisms, compasses, ship's figureheads, maritime-themed paintings and engravings, ancient sea charts, and historical documents on display on walls and floors.

Torre del Oro
A dodecagonal military watchtower built in the 13th century to control access to Seville via the Guadalquivir river, with a name referring to its golden shine due to its building materials.

Hospital de la Santa Caridad
A Roman Catholic baroque charity hospital building, dedicated to Our Lady of Charity, founded in 1674 and still caring for the aged and infirm, featuring a chapel with sumptuous baroque sculpture and eight paintings commissioned from Bartolomé Esteban Murillo.

Seville Royal Shipyard
A defensive wall and historic shipyard used by the Crown of Castile since the 13th century, originally built to construct and maintain warships for naval battles, and later used for various other purposes, including storage and jail facilities.

Teatro de la Maestranza
A historic opera house, Teatro de la Maestranza is a premier cultural venue in Spain, mainly hosting opera performances, as well as Zarzuela and other musical acts. The theatre is home to the Royal Seville Symphony Orchestra and the Choir of the Friends' Society of the Maestranza Theatre.

Plaza de toros de la Maestranza
A 12,000-capacity bullring built between 1749 and 1881, featuring a circular ring, ochavas, and a scenic Palco del Príncipe with a sculptural group above the entrance.
Download App
Experience this tour and many more with our mobile app. Available for iOS and Android.
Audio Preview
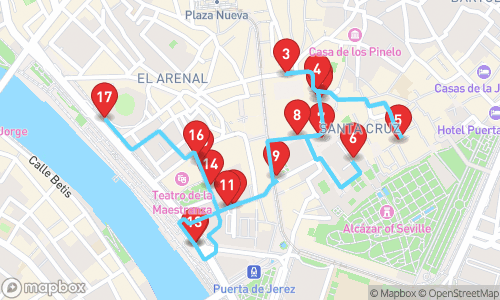
Tour Map
Quick Facts
- ✓GPS-guided navigation
- ✓Professional audio narration
- ✓Offline maps available
- ✓Premium content included
Why Choose This Tour
Expert Local Guide
Narrated by Jenny Multilingual, specializing in general tourism
Flexible Timing
Take the tour at your own pace, any time of day